E-commerce
What Is E-Commerce
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, encompasses the exchange of goods, services, funds, and data over the Internet. Leveraging technology like websites, apps, and social media, it revolutionizes how businesses connect with global consumers. This dynamic industry includes online marketplaces, apps, and social platforms, enabling versatile buying and selling experiences from anywhere with internet access.
With an estimated 2.14 billion online consumers worldwide, the impact of e-commerce is profound. This shift in consumer behavior has made e-commerce a crucial part of retail strategies for companies of all sizes. It empowers businesses to scale operations and reach a broader customer base globally.


What Is An E-Commerce Business?
An e-commerce business is a company that generates revenue by selling products or services online. This means they operate through digital platforms like websites, social media, and email rather than traditional physical stores. For example, an e-commerce business might specialize in selling software, clothing, and household items, or even provide services like web design.
What makes e-commerce unique is its flexibility and accessibility. You can run an e-commerce business from anywhere with an internet connection, making it an attractive option for entrepreneurs. Whether you choose to operate solely through a website or utilize various online channels like social media and email for marketing and sales, e-commerce offers a versatile platform to reach and engage with customers globally.

What Is An E-Commerce Website
An e-commerce website is essentially your digital store on the internet, where buying and selling transactions take place. It serves as the virtual storefront where customers browse products and make purchases. Think of it as your online store’s product display shelves, sales representatives, and checkout counter all rolled into one digital platform.
Businesses have various options when it comes to setting up an e-commerce website. Some may opt for a branded store experience on established platforms, leveraging their infrastructure and customer base. Others may choose to build their own dedicated e-commerce site with a unique domain, allowing for full customization and control over the shopping experience. Alternatively, businesses might adopt a multi-channel approach, utilizing both their website and external platforms for broader reach and sales opportunities.
How Does E-Commerce Work
E-commerce works by seamlessly connecting buyers and sellers through electronic channels, enabling transactions across various devices and platforms. When a customer makes a purchase, whether for physical goods or digital products like PDFs or online services, the online retailer facilitates delivery through shipping, store pickup, local delivery, or digital delivery methods.
The process begins with customers accessing an e-commerce platform, such as a website or social media channel, to browse products and services. Upon selecting items and adding them to their cart, customers proceed to the payment stage, where a payment processor facilitates the exchange of funds for goods or services. Once the transaction is successful, customers receive confirmation notifications via email or SMS, along with printable receipts for their records.
For physical goods, the seller then ships the items and provides customers with tracking information for their orders. If the transaction involves a service, the service provider contacts the customer to schedule and fulfill the service as per the agreement. Behind the scenes, e-commerce platforms manage the entire process, from listing products to order management, inventory updates, payment processing, and fulfillment coordination.
This streamlined process leverages technology to create a seamless shopping experience for customers while empowering businesses to efficiently manage sales and operations. With millions of transactions processed daily globally, e-commerce continues to evolve, offering innovative solutions and enhancing convenience for both buyers and sellers in the digital marketplace

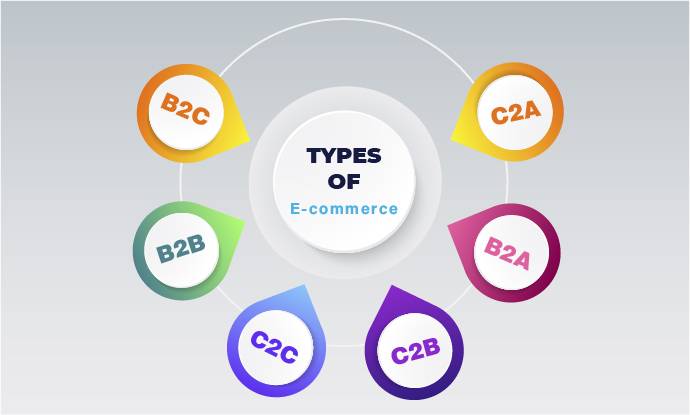
What Are The Types Of E-commerce
E-commerce encompasses various types that cater to different business models and customer needs. The primary types include:
- Business-to-consumer (B2C): This type involves transactions between businesses and individual consumers. It’s the most common form of e-commerce, seen in online retail stores where consumers purchase products directly from sellers.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses, where one business sells products or services to another. It’s prevalent in industries like manufacturing, where companies procure raw materials or components from suppliers.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers. Platforms like eBay and Craigslist enable individuals to buy and sell products or services directly to each other.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): In C2B e-commerce, individual consumers offer products or services to businesses. This model is common on freelancing platforms, where individuals provide services like graphic design or content creation to businesses.
- Business-to-Government (B2G): B2G e-commerce involves transactions between businesses and government entities. It includes services like procurement portals, where businesses bid for government contracts
- Consumer-to-Government (C2G): C2G e-commerce refers to transactions where individual consumers provide services or pay taxes to government agencies through online platforms.
- Government-to-Consumer (G2C): G2C e-commerce involves government agencies providing services or selling products directly to individual consumers through online platforms. This type is increasingly common in areas like online government services, tax filings, and public utility payments.
Each type of e-commerce has its own unique characteristics and target audiences, contributing to the diverse landscape of online commerce.
Different categories of e-commerce platforms and digital sales channel
Selling online offers a multitude of avenues to connect with consumers, ranging from proprietary channels like personalized online stores to leveraging third-party platforms. Each approach carries distinct advantages and drawbacks, prompting many online sellers to adopt an omnichannel strategy, utilizing multiple sales channels simultaneously.
1. E-commerce Platforms:
E-commerce platforms serve as robust solutions for generating revenue through personalized websites. These platforms empower individuals, creators, and businesses to establish their online presence seamlessly and integrate with physical stores if needed.
Benefits: E-commerce platforms provide extensive customization options, allowing businesses to create unique brand experiences. They also offer comprehensive analytics and reporting tools for performance tracking and optimization.
Challenges: Independent website selling necessitates active marketing endeavors to drive traffic and convert leads into sales. Managing inventory, fulfillment, and customer support independently can also be resource-intensive.

2. Online Marketplaces:
These platforms serve as bustling marketplaces where sellers can showcase their offerings to an engaged audience. Prominent examples include Amazon and Etsy, which double as powerful search engines for product discovery.
Benefits: Marketplaces provide instant access to a large customer base, eliminating the need for extensive marketing efforts. They also handle logistics, payment processing, and customer support, reducing operational burdens for sellers.
Challenges: Despite the visibility, building a distinct brand identity can be challenging within the confines of a marketplace. Sellers may face stiff competition, and platform fees and policies can impact profit margins.
3. Social Selling Channels:
Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram provide in-platform selling features, allowing businesses and personal brands to directly engage with their audience. This approach eliminates the need for a standalone e-commerce website for those preferring a streamlined online presence.
Benefits: Direct sales to existing social media audiences simplify the sales process and eliminate the need for separate marketing efforts. Social platforms also offer robust targeting options for reaching specific customer segments.
Challenges: Relying solely on social media platforms risks losing access to audiences if accounts are compromised or platforms undergo significant changes. Additionally, social selling may lack the depth of features and customization available on dedicated e-commerce platforms.
Email Us For More Information
E-mail Us
Admin@eclub.pk
